In an era of increasing cyber threats, protecting personal data has become a priority for companies worldwide. Effective data management requires the implementation of modern strategies and tools. Let’s explore practical approaches to data protection in the digital age.
Data Audit and Inventory
The first step in effective data management is conducting a thorough audit and inventory. Companies need to know what data they have, where it’s stored, and who has access. Regular audits help identify potential security gaps and minimize the risk of data breaches.
Data Encryption
It encryption is one of the most effective ways to protect information. Data should be encrypted both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access. Modern encryption algorithms ensure that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to third parties.
Access and Identity Management
Controlling access to data is crucial for its protection. Companies should implement the principle of least privilege, meaning employees only have access to the data necessary for their roles. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should also be used to enhance security.
Regular Updates and Security Patches
Software used for data storage and processing must be regularly updated to protect against the latest threats. Companies should track new security vulnerabilities and promptly implement available patches.
Employee Training
Even the best technologies cannot replace well-trained employees. Companies should regularly train their teams on best practices in data protection. Employees need to be aware of threats like phishing and know how to respond.
Using Threat Monitoring and Detection Tools
Network monitoring and threat detection tools can help quickly identify and respond to suspicious activities. These systems use advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence to analyze network traffic and detect potential threats in real-time.
Conclusions
Protecting personal data in the digital age requires a comprehensive approach that combines technology, procedures, and employee education. Regular audits, data encryption, access management, software updates, training, and advanced monitoring tools are essential to effectively protect data from increasing cyber threats. Companies investing in these strategies not only secure their data but also build customer trust and comply with legal regulations, which is crucial in today’s world.
In May 2018, the introduction of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) initiated a groundbreaking moment for the protection of personal data in the European Union. GDPR not only revolutionized the way personal data is protected within the EU but also had a significant impact on companies worldwide, promoting a uniform data protection standard across all member states.
Harmonization Leaps: From Fragmentation to Coherence
Before GDPR, diverse regulations in the EU challenged international enterprises. This created legal uncertainty and barriers to activity. GDPR introduced uniform rules, simplifying data management for companies. It also enhanced privacy protection for EU citizens.
Strengthening Citizens’ Rights and Operational Transparency
GDPR strengthened data subjects’ rights, introducing key mechanisms. These include the right to be forgotten, data access, and rectification. These initiatives boosted control over personal data. They also promoted transparency in organizational operations.
Global Impact of GDPR: Beyond EU Borders
GDPR significantly impacts not only enterprises operating within the European Union but also those outside its borders. Companies from outside the EU that process the data of EU citizens for offering goods or services, or monitoring their behavior, must also comply with GDPR. This global reach makes GDPR a de facto international standard for data protection.
The introduction of GDPR inspired many countries to review and improve their data protection regulations. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the General Data Protection Law in Brazil (LGPD) draw from GDPR experiences, aiming to raise data protection standards in their territories. GDPR has become a global benchmark for data protection regulations, promoting high standards of personal data protection worldwide.
Enterprises Facing New Challenges
Implementing GDPR required international enterprises to adjust their data protection policies and procedures, which was a challenge for many. However, these initial investments in GDPR compliance will bring long-term benefits, increasing consumer trust and promoting a safer digital environment.
The Future of Data Protection: GDPR as the Standard
GDPR not only unified the digital market in the EU but also raised the bar for personal data protection worldwide. As a living document, GDPR will likely evolve to meet new technological and social challenges, continuing to inspire a global approach to privacy and data protection.

Inspiring Global Standards
GDPR sparked a global discussion on data protection, highlighting international cooperation’s importance. The exchange of best practices is crucial as the digital economy transcends borders. GDPR serves as a model, showing that data protection and individual rights can coexist with innovation and economic growth.
Further Challenges and Opportunities
Although GDPR has established strong foundations, many challenges lie ahead. The development of technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) poses new privacy and data protection questions for GDPR. In response, EU institutions and supervisory authorities must continually adjust interpretations and guidelines to ensure that GDPR continues to achieve its goals in a rapidly changing technological world.
Education and Awareness: Keys to Success
The key to GDPR’s success is education and raising awareness. It’s vital for both businesses and citizens. Understanding rights and obligations is essential. This builds a culture where privacy is a fundamental right. It should not be seen as an option. Organizations gain a competitive edge by treating data protection as integral. This builds trust and customer loyalty. They see it as part of their business strategy.
Summary: GDPR as the New Standard for Data Protection
GDPR has become a milestone in personal data protection. It established strong, uniform frameworks for Europe. It also inspires changes worldwide. Its impact on global enterprises is significant. It affects regulations in other countries and technological development. This underscores the importance of an adaptive stance towards data protection. A proactive stance is also crucial. We are now entering a new digital era. GDPR will continue to play a key role. It shapes the future of privacy and personal data protection. Operates on a global level. It sets standards for other countries and regions. These countries and regions will strive to meet these standards.
The modern world is rapidly moving towards digitizing various aspects of our lives. Not only are media, education, and shopping transitioning into the virtual space, but so are official documents. One flagship example of this trend is the mObywatel app, which is growing in popularity in Poland year by year. What features does mObywatel offer? What new regulations does the latest act introduce? Here’s a comprehensive guide to the world of mObywatel.
What is mObywatel?
mObywatel is an innovative mobile app developed by the Polish government that allows users to store and use electronic versions of official documents, such as ID cards, school or student IDs. This tool makes life easier for millions of Poles, eliminating the need to carry traditional versions of these documents.
Safety First
Personal data security is a priority for the app’s developers. Data processing in mObywatel is carried out with full respect for users’ privacy. Information such as name, surname, PESEL number, or user’s photo comes from official state registers, ensuring their authenticity. Importantly, this data is protected with advanced encryption technologies, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. A key security feature is also the requirement to enter a personal PIN code before accessing the app.
Rich App Capabilities
mObywatel is not just an electronic ID. The app allows you to:
- Verify your identity using a smartphone at various institutions and customer service points,
- Handle a variety of official matters online,
- Check your penalty points and driver’s entitlements,
- Electronically confirm vaccinations, including against COVID-19,
- Show electronic school and student IDs,
- And many other features that make citizens’ daily lives easier.
The Latest Act and mObywatel
Recent changes in legal regulations have further expanded the scope of rights and functionalities of the mObywatel app. The new act, which came into effect, allows the use of mObywatel in a broader range of institutions and offices, making the app more functional and adapted to users’ needs. It’s worth following regular updates to stay up-to-date with the latest features and possibilities the app offers.

mObywatel in an International Context
Looking at solutions from other countries, we see that the trend of digitizing public services is global. Estonia, for example, is often regarded as a pioneer in this field due to its e-Residency and e-ID program. Estonian citizens use electronic ID cards that offer a wide range of online services, from business operations to voting in elections.
In Asia, Singapore has impressed with its SingPass system, which allows residents easy access to government services, such as applying for benefits or reviewing medical results. Sweden, on the other hand, developed the BankID system, which has become the standard for online identity verification in many situations, both in commercial and public services.
However, not all systems were adopted without controversy. India’s Aadhaar system, although greatly simplifying bureaucratic processes for nearly 1.3 billion citizens, raised some concerns about privacy and data security.
mObywatel blends ID features with a broad array of services in global efforts. It’s Poland’s response to the global digitization trend, offering Poles a modern tool tailored to local needs and standards.
Summary
In the digital age, mObywatel simplifies daily tasks and contact with government agencies. Thanks to its high level of security and continuous updates, it becomes an essential part of every Pole’s smartphone. By using it, we become active participants in the digital world, where traditional methods give way to modern solutions.
Since its introduction in 2018, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has gained significant attention. It has become one of the main topics of debate concerning privacy protection. Many myths and misconceptions have arisen around GDPR. Here are ten of them that are worth debunking!
GDPR only applies to large companies.
False! GDPR applies to any organization or individual who processes personal data of European Union residents, regardless of the company size or type of activity.
Breaches in GDPR always result in massive fines.
While significant fines are possible for non-compliance with GDPR, in reality, regulatory authorities aim to first educate and assist companies in adhering to the regulations.
Personal data is just a name and surname.
Mistake! Personal data encompasses any information that can be attributed to a specific individual. This includes an email address, phone number, location, or data related to online activity.

Consent is always needed to process data.
Not always. There are various legal grounds for data processing, including contract execution or the legitimate interest of the administrator.
Data can be stored indefinitely.
False. According to GDPR, personal data should only be stored for as long as necessary for the purposes for which it was collected.
GDPR only applies to companies based in the EU.
It applies to any company that offers goods or services to EU residents, regardless of its location.
GDPR prohibits the storage of backup copies of data.
This is not true. Backup copies are essential for data security, but they need to be adequately protected and in compliance with GDPR principles during their storage.
If a company uses a third-party service to process data, it’s not responsible for any breaches.
Wrong assumption. The company that outsources data processing still bears responsibility for its security.
GDPR only concerns electronic data.
Not just that. GDPR pertains to data processed both in electronic and paper forms.
Every GDPR breach must be reported to the relevant authorities.
Not all. Reporting is only required in cases of breaches that might lead to a “high risk to the rights and freedoms of natural persons.”
In conclusion, GDPR introduced many significant changes in the field of personal data protection. To comply with regulations appropriately, it’s essential to distinguish facts from the myths circulating around this regulation.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) was introduced by the European Union to address growing concerns about privacy and data protection in a world increasingly dominated by technology. The implementation of these regulations has revolutionized the way businesses collect, process, and store data. But what exactly do these changes mean for companies operating in Europe? And what are the consequences of not adhering to them?
Portuguese Hospital Fined by CNPD
In 2018, the Comissão Nacional de Protecção de Dados (CNPD) fined Barreiro-Montijo Hospital 400,000 euros. This Portuguese authority oversees personal data protection. The incident is a major example of GDPR enforcement in the European Union.
The Barreiro-Montijo Hospital Center in Portugal faced penalties for numerous and grave violations. An inspection revealed that the hospital lacked internal regulations for creating accounts and managing access to medical data. Moreover, there was a failure in taking steps to remove accounts of employees who had left the hospital. Additionally, patient data access was mishandled, leading to breaches.
Permission Management: How to Avoid Similar Issues?
Modern institutions, particularly those in the medical sector, must give special attention to permission management. Adequately structured and consistently implemented procedures in this field can not only shield institutions from potential sanctions but also elevate the overall level of information security.

Introducing a clear security policy is the cornerstone. It meticulously dictates who can access information and how much. Yet, that’s just the beginning.
These procedures should encompass not only the granting and revoking of permissions but also their regular reviews and updates. As the organizational structure changes and the roles of employees shift, permissions should be readjusted to continually reflect actual needs and maintain optimal security levels.
Moreover, it’s prudent to introduce systems monitoring access and user activities. Such systems not only bolster security by detecting unauthorized access but also act as audit tools, potentially providing evidence in the event of violations.
In conclusion, training staff on security policies and permission management is vital. Even the most robust system can falter if employees lack awareness of their roles and responsibilities in data protection.
Conclusion
The penalty given to Barreiro-Montijo Hospital in Portugal is a warning. It highlights the importance of permission management. It also emphasizes the consequences of GDPR violations. Safeguarding personal data has multiple purposes. It’s not just about avoiding fiscal penalties. It’s mainly about building trust with customers and patients. Institutions hold many people’s data. In today’s era, data protection is essential. It’s not a luxury.
The first, and perhaps most basic, mistake is a lack of awareness or understanding of the GDPR. Despite the regulation having been in effect for several years, some companies still do not fully understand it. They are unsure what these regulations mean for their business. The GDPR is complicated and requires companies to adhere to a number of specific rules regarding personal data. Without a proper understanding of these rules, companies are at risk of non-compliance and potential penalties.
Improper Data Storage and Security
Another common mistake is the improper storage and security of personal data. These data must be stored securely to prevent their loss or theft. In practice, companies need to implement appropriate security measures, such as encryption. They also need to regularly update and test their security systems.
Lack of Effective Data Retention Policy
A lack of an effective data retention policy is another mistake that companies frequently make. The GDPR mandates companies to retain personal data only for the duration necessary for the purposes of its collection. They should not keep the data longer than required. Without a clearly defined data retention policy, companies might keep data either too long or not long enough. Such practices can result in non-compliance.
Failure to Update Data Protection Policies
Data protection law is a dynamic area that is constantly evolving and changing. If companies do not regularly update their policies and procedures, they may easily end up in a situation not compliant with the latest requirements. This means that companies must actively monitor changes in the law and adjust their practices accordingly.
Consequences of Mistakes
Financial Penalties
One of the most severe consequences of non-compliance with the GDPR is financial penalties. If organizations violate GDPR regulations, they can incur fines. These can reach up to 20 million euros or up to 4% of their annual global turnover, depending on which value is higher. For example, in 2019, the UK’s Information Commissioner’s Office imposed a fine of 204 million euros on British Airways for GDPR violations.
Loss of Customer Trust
The loss of customer trust is another important consequence of improper data management. When customers discover that their data wasn’t adequately protected, they might decide against using the company’s services in the future. Such a loss of trust can lead to loss of customers and decrease in sales.

Potential Business Losses
At the end, non-compliance with GDPR and improper data management can lead to huge business losses. Not only do these encompass potential fines and the loss of customers, but they also cover costs tied to rectifying mistakes. This includes implementing new security systems and training staff.
How to Avoid Common Mistakes
Detailed Understanding and Compliance with GDPR Rules
The first step to avoiding these mistakes is understanding and complying with the GDPR rules. Companies should make sure that all individuals handling personal data are familiar with GDPR regulations. They should also ensure these individuals know how to apply these rules. Data protection training should be conducted regularly to ensure that staff are up to date with the latest regulations.
Implementation and Compliance with an Effective Data Retention Policy
Companies should also create an effective data retention policy. This policy should detail how long they should store various types of data. This policy should be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure its compliance with current regulations.
Regular Reviews and Updates of Data Policies and Procedures
Another important step is regular reviews and updates of data-related policies and procedures. This includes not only data retention policy but also data security policy and consent processing procedures. Regular reviews will help ensure that the company’s policies and procedures are up to date with the latest legal requirements.
Training Staff in GDPR Rules and Data Retention
The last but not the least step is ensuring that all staff are adequately trained in GDPR rules and data retention. This will not only help prevent mistakes but also help employees understand why these rules are so important and what could be the consequences of not adhering to them.
Conclusion
Compliance with GDPR and effective data retention are key to maintaining legal compliance and protecting customer trust. By avoiding the most commonly made mistakes, companies can better manage their data, minimize risk, and maximize the benefits of data ownership. It’s a process of continuous learning and adaptation, but the effort is worth it considering the potential consequences.
Welcome to Wizards! We are specialists in data protection, providing effective tools for detecting, anonymizing, and retaining personal data. Our services ensure full compliance with GDPR in terms of personal data protection.
We have 25 years of experience in creating systems for handling sensitive data across various sectors. We utilize cutting-edge technologies such as big data and machine learning. As committed developers and co-owners of the company, we understand the challenges related to GDPR compliance. We want to relieve other specialists from these challenges. This allows them to focus on their own tasks.
f you are looking for tools to manage personal and sensitive data, please contact us. Let’s schedule a conversation. It’s the first step to ensure your company can avoid potential fines. Contact us today.
Understand the Consequences of Violating GDPR
Understand the Consequences of Violating GDPR: Non-compliance with Rules such as Improper Data Retention or Incorrect Anonymization Can Lead to Administrative Sanctions and Financial Penalties.
In accordance with Article 83(5) of the GDPR, violations of the provisions concerning general principles, such as retention or minimization, may result in the imposition of a monetary penalty of up to 20,000,000 EUR or, for enterprises, up to 4% of the total global annual turnover of the previous fiscal year. In the case of both amounts, the higher one applies.
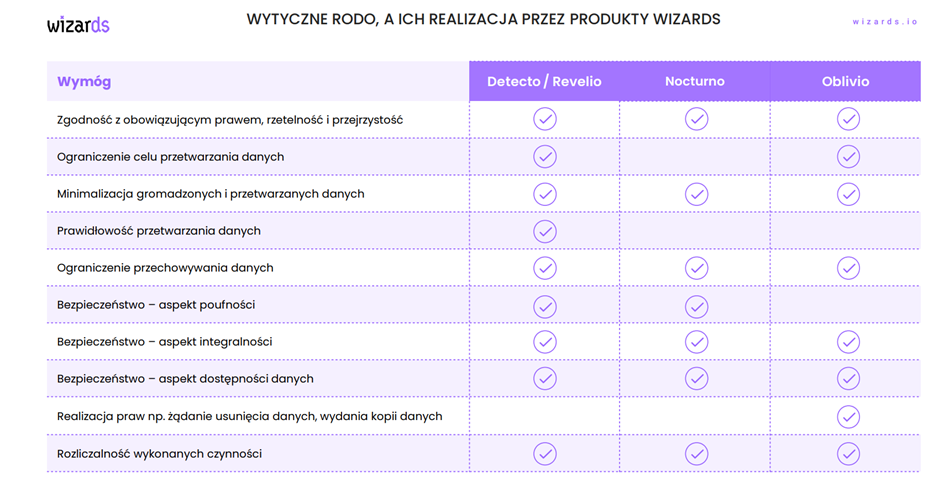
The key aspects of data processing are multifaceted. They include compliance with the law, fairness, and transparency. Purpose limitation and data minimization are also vital. Additionally, accuracy and security are crucial, encompassing aspects such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It is also essential to consider the rights, such as deletion or copying of data, and the responsibility for processing.
Check our tools
By choosing Wizards, you protect your company from potentially massive costs arising from GDPR violations. This can be illustrated by the example of British Airways, which was fined 204 million euros for personal data breaches in 2019. Through our collaboration, you can be assured of the safety of your finances, business, employees, and customers.
- Detecto, a system that monitors personal and sensitive data in databases, supporting anonymization and retention processes.
- Revelio, an effective solution for identifying personal and sensitive data in documents and email, promoting the digitization of business processes.
- Nocturno, an advanced system for anonymizing personal data in IT systems, maintaining data consistency between different systems.
- Oblivio, a dedicated system for managing personal data retention within an organization.
With Wizards, you’ll ensure GDPR compliance, protect your company from costly penalties associated with regulation breaches, and safeguard not only your finances but also your business, employees, and customers.

Practical Application of Our Tools
Our tools have real-world applications that translate into the daily functioning of companies. Below, we present specific examples.
Detecto. A telecommunications company was using an advanced ERP solution from one of the leading providers. During an audit, IT had to locate places within the ERP system where personal data were stored. Detecto from Wizards scanned the system’s databases and provided a report with the locations of personal and financial data.
Revelio. In an insurance company, despite using various security tools, there was a leak of customer data and financial information. Revelio helped identify over 1000 files containing more than 100 customer names along with bank account numbers, gathered in the SharePoint repository and on personal computers.
Nocturno. A client was using 20 different IT systems. To handle this complexity, Wizards Nocturno automated the process of creating test and development environments. During this creation, the system ensured that personal and sensitive data were anonymized. Moreover, this anonymization did not affect the qualitative and quantitative parameters of the data. As a result, it allowed for secure testing and software development.
Oblivio. A public institution was processing the data of its employees. Oblivio helped identify which data should be deleted in accordance with data retention regulations. The tool also took care of the anonymization of employee data that needed to be removed from the human resources systems.
Would you like to learn more about the practical applications of our tools? Contact us for a conversation. We have dozens of other examples!
Collaboration Models
Secure your business with one move. Discover our collaboration options and schedule a conversation to safeguard your enterprise.
Collaboration Options:
- Detecto – Identification of personal data in three selected databases for 10,000 PLN.
- Revelio – Identification of personal data in shared resource files (up to 100,000 files) for 10,000 PLN.
- Oblivio – Information on the quantity of personal data subject to retention, stored in your database (applies to 1 process, max 3 systems) for 10,000 PLN.
We offer one-time use options or subscriptions for a period of a month or a year.
With us, it’s worth it!
RODO regulations can be difficult to understand and implement. At Wizards, we focus on accessibility and effectiveness. Our tools, Detecto, Revelio, Nocturno, and Oblivio, tailored to your needs, provide efficient personal data management and full compliance with GDPR.
Don’t let the fear of GDPR hinder your company’s growth. With us, you gain confidence and security, enabling you to focus on what’s most important – your business. So choose Wizards, choose the only proper protection. Then schedule a conversation with us today and safeguard your company from the consequences of GDPR violations.
Processing personal data is an integral part of the digital reality. Companies face many challenges. Cybercrime poses a serious threat. Society is becoming more aware of its privacy. Legal regulations, including GDPR, set specific requirements. Companies need to approach them flexibly and responsibly. However, it’s hard to determine the impact of these elements on the development of artificial intelligence (AI).
Cybercrime
Cybercrime is a significant challenge in today’s world. The intensity of this problem is increasing every year. In business language, terms such as hacking attacks, phishing, and ransomware have become common. Companies processing personal data must invest in IT security systems. They also need to train their teams. This allows them to effectively counter threats. Data security is a priority for every business.
Social awareness of privacy
The right to privacy is a basic human right. In the era of digitization, it becomes even more important. Customers are increasingly aware of their rights. They expect companies to be transparent in data processing. Companies that do not meet these expectations risk losing customers’ trust. This, in turn, can lead to a loss of their loyalty.
The right to privacy is a basic human right. It enables control over information about oneself. It protects against improper use. GDPR, as a European regulation, crucially treats this right.
GDPR obliges companies to protect the processed data, and companies must inform individuals about the purposes of processing their data. They also must allow them access to these data.
GDPR introduces the right to be forgotten, which means that an individual can request the deletion of their data in certain situations. Additionally, the right to data portability is another element of GDPR that allows data to be transferred between service providers.
So, the right to privacy in the context of GDPR is control over personal data. It’s protection against their improper processing.
Increasing legal requirements
GDPR is a key regulation regarding data processing. It introduces many requirements that companies must meet. Severe sanctions threaten violations of these regulations. They can reach up to 20 million euros. Alternatively, it can be 4% of the company’s global turnover. This demonstrates the seriousness of the right to privacy in the European Union. Companies, therefore, need to dedicate resources to ensure GDPR compliance. This is also necessary for other legal provisions.

GDPR and artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is an area of progress and innovation. However, it must comply with GDPR regulations. Companies are obligated to inform customers about the processing of their data by algorithms. They also need to provide a “right to explanation” for automatic decisions. Such requirements can slow down the development of AI. At the same time, they can encourage the creation of more “transparent” and ethical AI models.
Solutions and the future
Challenges in data processing are significant, but surmountable. New technologies can increase privacy and data security. Companies investing in advanced AI must integrate GDPR principles at the design stage. This is known as privacy by design. Training employees and building a culture of respect for privacy is key. This applies to all levels of the organization.
Conclusion
Data has become the new “gold” in our world. The ability to manage it is the key to success. GDPR may pose a challenge, but it also offers an opportunity to build trust. Increasing customer loyalty is possible thanks to this. We observe dynamic development of technology, including artificial intelligence. An approach to data that combines innovation and ethics will be the key to future success. What do you think, who will win the battle, GDPR or artificial intelligence?

It would be hard to miss all the articles on the topic of GDPR and all the various, terrifying sanctions that could be put upon an entity for non-compliance. Few, however, delve into important details, such as the significance of anonymization or data retention, which allow for avoiding all these sanctions and make the work of developers significantly easier. For this reason, we decided to explain in an accessible way what anonymization and retention of personal data are and show why their proper implementation is of such importance in the software development process. Today, let us tackle anonymization.
What is anonymization?
Anonymization is a process that allows you to permanently remove the link between personal data and the person to whom the data relates. Thanks to this, what was previously deemed as personal ceases to be that.
What does it look like in practice?
The definition above becomes less complicated when presented with an example. Let us imagine, for example, Superman – a comic hero from Krypton who wants to hide his identity and blend in with the crowd.
| Name | Superman |
| Occupation | Superhero |
| Origin | Krypton |
During the anonymization process, Superman enters the telephone booth, puts on glasses and a tweed suit, and becomes Clark Kent, a reporter from Kansas.
| Name | Clark Kent |
| Occupation | Reporter |
| Origin | Kansas, USA |
Through the anonymization process, Superman’s data turned into Clark Kent’s, and there is no connection between these two people. This is fictitious data that can be safely used, e.g. in test environments.
The example above illustrates the process of anonymization itself. Let us now consider why it is important that the anonymization is of good quality.
Irreversibility
The foundation of anonymization is its irreversibility. We should never be able to find out what the original data looked like, based on the anonymized data. Clark’s associates should not be able to discover his true identity.
When we anonymize a data set, usually only a fragment of the data will undergo change. However, we must ensure that non-anonymized data does not allow the anonymization process to be reversed for the entire set. In our example, we would not have to change Superman’s favorite color. However, if we do not anonymize his origin, we would certainly cause a sensation.
True to reality
An important qualitative measure of anonymization is also how well it imitates reality. If Superman and all other people in the data set are anonymized as follows:
| Name | X |
| Occupation | Y |
| Origin | Z |
we have no doubt that the process is irreversible, but its usefulness is questionable. Person X does not look like someone who exists in reality, and the nature of the original data has not been preserved. The length of the names were not preserved, and the data itself looks unbelievable with all of the people having the same name. In the case of IT systems, the tester using such data would run into a lot of issues, he would not even be able to distinguish between people.
Repeatability
Another feature of good anonymization is its repeatability. When anonymizing the data set, we want to make sure that each time the data set would be anonymized in the same way. We want Superman to always become Clark Kent, no matter whether it’s the first or the tenth anonymization. This is especially important from the point of view of Quality Assurance. Testers often create test cases based on specific data. If this data were changed every time, the tester’s work would certainly be more difficult!
Integrated systems
Today’s IT world is represented by countless systems connected with each other. Hardly any application can function as a single organism. Systems connect with each other, exchanging data and using each other’s services. Therefore, when approaching anonymization, we must consider the process not only for one system, but for many systems at once. The challenge is for anonymized data to be consistent throughout the entire ecosystem. This means that if the Daily Planet (Clark’s workplace) has a human resources system and a blog, then in both applications Superman will become Clark Kent.
Efficiency
The last key parameter affecting the quality of anonymization, from my point of view, is performance. IT systems process huge data sets measured in gigabytes or even terabytes. Anonymization of such databases can be time consuming, therefore, we must ensure not only security but also good speed of the anonymization process. One of the things Superman learned after arriving on Earth is that time is money. This saying rings even more true in the case of modern IT.
I invite everyone interested in the topic of data retention to read my next article, which I plan on publishing shortly.
Artur Żórawski, Founder & CTO

Soon it will be twenty years since I joined the world of IT. During this time, I have observed how the environment has changed, how development processes have developed and what new tools have been used. Over time, many processes, including repetitive tasks, were automated. Companies implemented Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery. All of this change has been motivated by a single thought: let software developers focus on system and business development.
Enter GDPR
The entry of GDPR into life shook the IT world and changed the rules of the game. The development process became more complicated and operating on personal data became a big risk that had to be addressed. Working in a software house, we saw these issues clearly because they occurred in each of our projects. In theory, we were prepared for GDPR. We completed the appropriate courses and the company was armed with documents and records. In practice, it turned out that legal restrictions and the uncertainty associated with the entry of this regulation into force impacted our everyday work. Gone was my dream of unhindered development, where we could focus solely on producing quality software.
Shortly after the appearance of GDPR regulations, we started looking for available solutions. The tools that we were able to find did not meet our project needs because every day we developed entire integrated ecosystems created in various technologies that exchanged personal data. I felt as if I had travelled two decades backwards in time.
Change of status quo
Ultimately, a group of people in the company emerged that set themselves the goal of changing the status quo. We knew what was required and how our plan could be implemented. We had never faced such a challenge before. Together, however, we managed to create a set of tools that ended up being a Godsend for us.
Anonymization of data
We started by anonymizing data in test environments. We created a tool that was able to handle many applications at once, taking into account the specificity of Polish law, and do its work efficiently.
The created solution was to support all of our projects, so high configurability and the ability to adapt to various requirements was the priority. We included anonymization in Continuous Integration processes and quickly implemented them in our projects. It turned out that the most painful aspects of GDPR are now handled automatically and no longer cause sleepless nights to the development team.
Retention of personal data
The next step was the retention of personal data, which is necessary in almost every system. Taking care of this aspect in a single application is easy. Performing data retention in ten integrated systems is much more difficult, and in a hundred – virtually impossible. It was clear to us that we did not want to repeat the same functionality in all systems that we produce. This is how another tool was born, relieving us of this burden.
Everything was back on track, just as I had dreamed. Fortunately, GDPR turned out to be only a bump on the road in our projects.
Wizards
With all of this in mind, we founded a startup. We came to the conclusion that the problems we had been dealing with were being experienced by many development teams, and we now had the ready solution.
That is why we decided to create Nocturno and Oblivio, about which you will be able to read more soon on our company profile.
Artur Żórawski, Founder & CTO of Wizards
